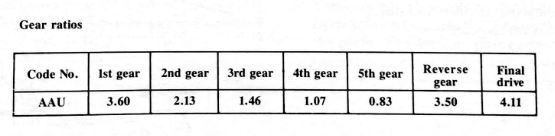
 [ezcol_1half]The Quantum Syncro is equipped with a hydraulically operated clutch. As in the past, an overcenter spring assists foot pressure when depressing the pedal.
[ezcol_1half]The Quantum Syncro is equipped with a hydraulically operated clutch. As in the past, an overcenter spring assists foot pressure when depressing the pedal.
To operate the clutch, brake fluid from the brake master cylinder reservoir is used. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the piston in the master cylinder forces fluid into the slave cylinder.[/ezcol_1half] [ezcol_1half_end]The piston in the slave cylinder moves the clutch release bearing and the clutch is disengaged.
There is a spring in the slave cylinder that insures that the clutch release bearing rests constantly on the clutch diaphragm spring. This feature eliminates the need for clutch adjustment.[/ezcol_1half_end]
 [ezcol_1half]The 016 transmission used in the Quantum Syncro is all new for Volkswagen.
[ezcol_1half]The 016 transmission used in the Quantum Syncro is all new for Volkswagen.
This transmission features synchronizers in all forward gears and also in reverse.
The standard production transmission was modified to allow the addition of a center differential and a driveshaft to the rear wheels.[/ezcol_1half] [ezcol_1half_end]This compact package requires only a minimum number of additional components which means only a small increase in weight.
Gear ratios for the 016 have been carefully determined to meet the needs of the Syncro.[/ezcol_1half_end]
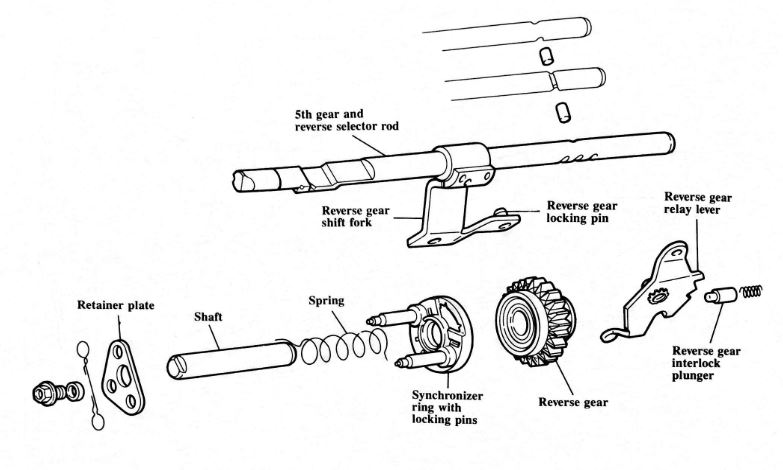
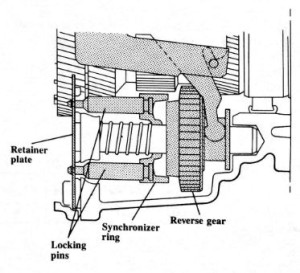 The 016 transmission features a unique synchronizer for reverse gear. This design uses a synchronizer ring with lock pins and a reverse gear with a tapered synchronizer surface.
The 016 transmission features a unique synchronizer for reverse gear. This design uses a synchronizer ring with lock pins and a reverse gear with a tapered synchronizer surface.
Because this is the only gear in the transmission that is not in constant mesh, a synchronizer is beneficial in allowing smooth and quiet engagement of reverse gear.
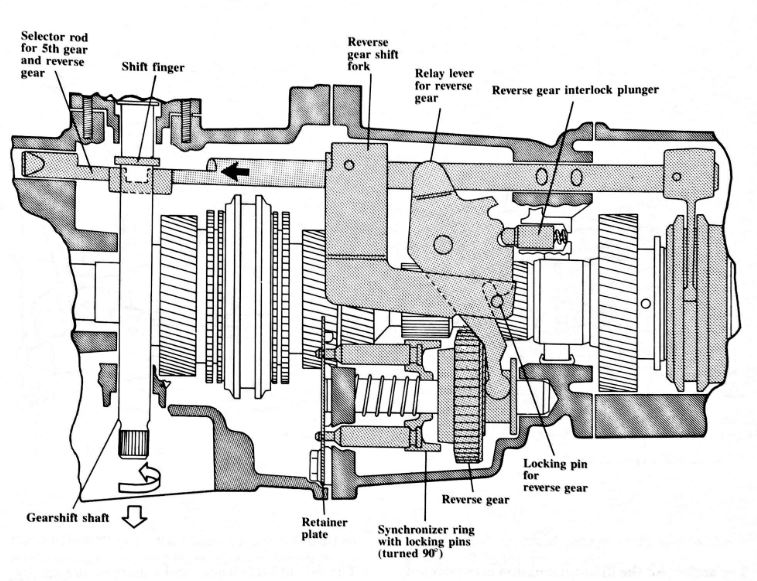 When reverse gear is selected, the gearshift shaft rotates, and the shift finger moves the selector rod for reverse to the left.
When reverse gear is selected, the gearshift shaft rotates, and the shift finger moves the selector rod for reverse to the left.
The locking pin on the reverse gear shift fork engages the relay lever, and the relay lever pulls reverse gear into engagement.
The retainer plate keeps the synchronizer ring from turning because the pins go through holes in the plate. The locking pins become centered in the retainer plate as spring pressure is exerted, and reverse gear is stopped so it engages quietly.
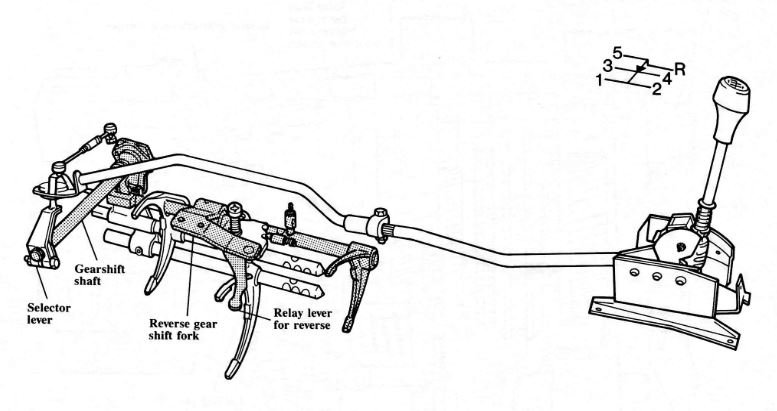 The shifter for the 016 transmission is connected to the gearshift shaft located inside the transmission housing cover. During gear selection, the shift finger on the gearshift shaft engages the appropriate selector rod.
The shifter for the 016 transmission is connected to the gearshift shaft located inside the transmission housing cover. During gear selection, the shift finger on the gearshift shaft engages the appropriate selector rod.
The detent for 5th gear and side pressure spring are incorporated into the gearshift shaft assembly.
Although the shift fork for 5th gear and the shift fork for reverse gear are located on a common selector rod, the detent makes it impossible to shift directly from 5th gear into reverse.
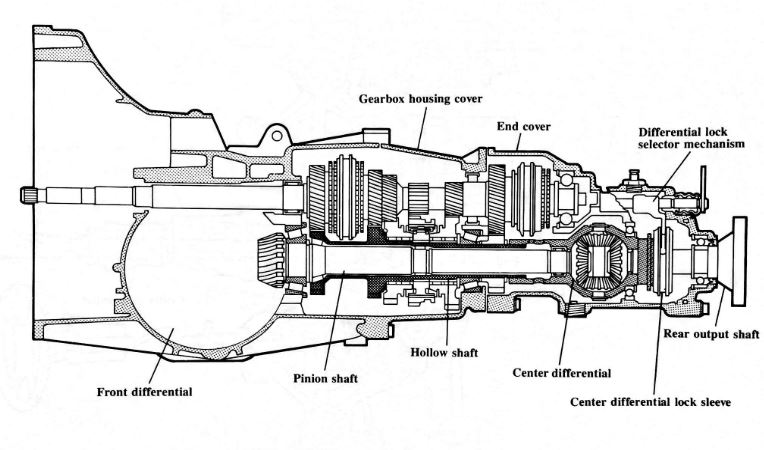 Power flow through the transmission is similar to conventional 5 speed transmissions, with one exception.
Power flow through the transmission is similar to conventional 5 speed transmissions, with one exception.
Inside the transmission, a hollow shaft delivers power through the gears to the center differential. Power is then transmitted to the front axle differential pinion shaft and to the driveshaft to the rear axle.
The pinion shaft is supported by a tapered roller bearing in the transmission housing and by two needle bearings, one in the hollow shaft and one in the center differential housing.